How To Install MySQL 5.7 on CentOS/RHEL 8
MySQL is an open-source relational database management system. It is being developed by Oracle Corporation. Its proven reliability, performance, and ease of use. MySQL is an important component of the LAMP and LEMP stacks.
Useful Articles:
- INSTALL MYSQL PASSWORD VALIDATION PLUGIN ON LINUX
- HOW TO CHANGE MYSQL PASSWORD POLICY LEVEL ON LINUX
- HOW TO CONFIGURE LOGANALYZER WITH RSYSLOG AND MYSQL ON CENTOS/RHEL 7/6/5
- SETUP RSYSLOG WITH MYSQL ON CENTOS/RHEL 7
- SETUP RSYSLOG WITH MYSQL ON CENTOS/RHEL 6/5
- FEW MYSQL COMMANDS IN LINUX
- INSTALL LAMP (APACHE 2.4, MYSQL 5.6, AND PHP 7.0) ON UBUNTU USING PPA
- INSTALL LAMP (APACHE 2.4, MYSQL 5.6, AND PHP 7.0) ON CENTOS/RHEL 7
In this article, I will explain to you how to install MySQL 5.7 on CentOS/RHEL 8.
Step 1: Add MySQL repository
First, you need to Disable MySQL from the default AppStream repository.
# dnf module disable mysql
Now, add MySQL repositories to your system.
# vim /etc/yum.repos.d/mysql-community.repo
Paste the below data into the MySQL repo file.
[mysql57-community] name=MySQL 5.7 Community Server baseurl=http://repo.mysql.com/yum/mysql-5.7-community/el/7/$basearch/ enabled=1 gpgcheck=0 [mysql-connectors-community] name=MySQL Connectors Community baseurl=http://repo.mysql.com/yum/mysql-connectors-community/el/7/$basearch/ enabled=1 gpgcheck=0 [mysql-tools-community] name=MySQL Tools Community baseurl=http://repo.mysql.com/yum/mysql-tools-community/el/7/$basearch/ enabled=1 gpgcheck=0
Step 2: Install MySQL 5.7
Now, the new MySQL repository is available on the system and we are ready to install MySQL 5.7 from the repository.
Disable MySQL 8 repository:
# dnf config-manager --disable mysql80-community
Enable MySQL 5.7 repository:
# dnf config-manager --enable mysql57-community
Now, you are ready to install MySQL 5.7:
# dnf install mysql-community-server
Step 3: Start MySQL Service
Now start MySQL service and enable to start on boot using the below commands.
# systemctl start mysqld.service # systemctl enable mysqld.service
Step 4: Set Root Password
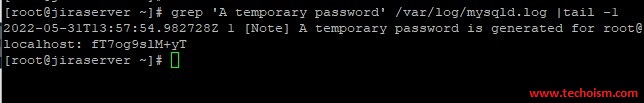
Before configuring the root user password we need to copy the temporary password for the root user.
# grep 'A temporary password' /var/log/mysqld.log |tail -1
Apply security on MySQL and also set the root user password.
# mysql_secure_installation
Enjoy it!